AI detectors analyze writing patterns to find machine-generated content, but their accuracy is inconsistent, with high false positives.
They should be used cautiously, alongside human review, not as the sole evaluation tool.
The operational mechanics of AI detectors
AI detectors use three main techniques to identify machine-generated content, focusing on specific text characteristics.
Language pattern analysis
AI detectors identify machine-generated text by looking for unique structural patterns, repetitive structures, generic language and lack of natural tone.
They compare text segments against models trained on human and AI-generated examples to pinpoint subtle machine traits.
Statistical models and measurements
AI detectors use statistical analysis, converting words to numbers. Key metrics are perplexity (text predictability) and burstiness (sentence variation).
AI text scores low on both; for instance, perplexity over 85 often means human authorship. These metrics help assess the authenticity of academic work.
Machine learning methods
AI detectors use machine learning and classifiers trained on vast datasets to identify subtle linguistic differences between human and AI text.
They use embeddings (numerical word vectors) to assess semantic coherence, achieving high accuracy (up to 99%). A key benefit is their adaptability as AI writing tools evolve.
AI detector accuracy
AI detection tool claims of near-perfect accuracy are often unreliable in real-world academic and professional use.
Accuracy rates and common issues
Despite company claims of high accuracy, independent studies show AI detectors are significantly flawed. A test of zeroGPT found 1–2% false positive rates, meaning students could be wrongly accused.
Other detectors have flagged up to 27% of authentic texts as AI-generated, leading one major evaluation to conclude the tools are "neither accurate nor reliable." OpenAI even discontinued its own tool after it achieved only a 26% success rate. The main struggle is that these tools cannot keep up with advanced models like GPT-4.
The errors AI detectors make
AI detectors make false positive (human-written flagged as AI) and false negative (AI-written goes undetected) mistakes, both of which have serious implications.
False positives disproportionately affect non-native speakers and neurodiverse individuals, as shown by one detector flagging the U.S. Constitution as 98.53% AI-generated.
False negatives occur when users exploit loopholes like paraphrasing or editing AI text. Detectors also struggle with short, non-essay formats, often flagging complex human writing while simpler AI styles slip through.
Interpreting detection results
AI detectors rely on trained patterns, not true language understanding. Treat scores as preliminary, not definitive. Platforms like Turnitin recommend combining scores with human judgment.
Use detection scores as one part of a balanced assessment, looking at other factors like writer style and tone shifts for responsible use.
Benefits and drawbacks of AI detection tools
AI detection tools offer benefits but also present significant challenges.
Main benefits of AI detectors
AI detection tools offer six main benefits:
- Speed/Efficiency: Rapid text analysis.
- Academic Integrity: Upholds ethical standards.
- Quality Control: Filters low-quality AI content.
- SEO Protection: Avoids search engine penalties.
- Legal Risk Reduction: Minimizes plagiarism/copyright issues.
- Streamlined Review: Focuses human attention on questionable parts.
They help academics maintain standards and institutions protect reputations, while organizations gain legal safety and efficient content review.
Problems and ethical issues
AI detectors have significant drawbacks: a high error rate, especially false positives that impact non-native English speakers and neurodiverse individuals.
They erode trust between students and educators and are easily bypassed. Over-reliance risks replacing human judgment, diminishing critical thinking and potentially violating regulations like FERPA, Title VI and ADA.
Benefits vs. drawbacks comparison
Here’s a side-by-side look at how the benefits and drawbacks stack up:
AI detection is a complex tool. While 84% of educators use AI, a quarter feel it causes more harm than good. Thoughtful use, prioritizing fairness and accuracy, is essential.
How to use AI detectors effectively?

Balance automation and human judgment for AI detection tools. They are part of a workflow, not final decision-makers.
AI detection in academic writing tools
AI detection is being integrated into academic integrity frameworks, often alongside tools like plagiarism checks and citation verification, to enhance trust and maintain standards.
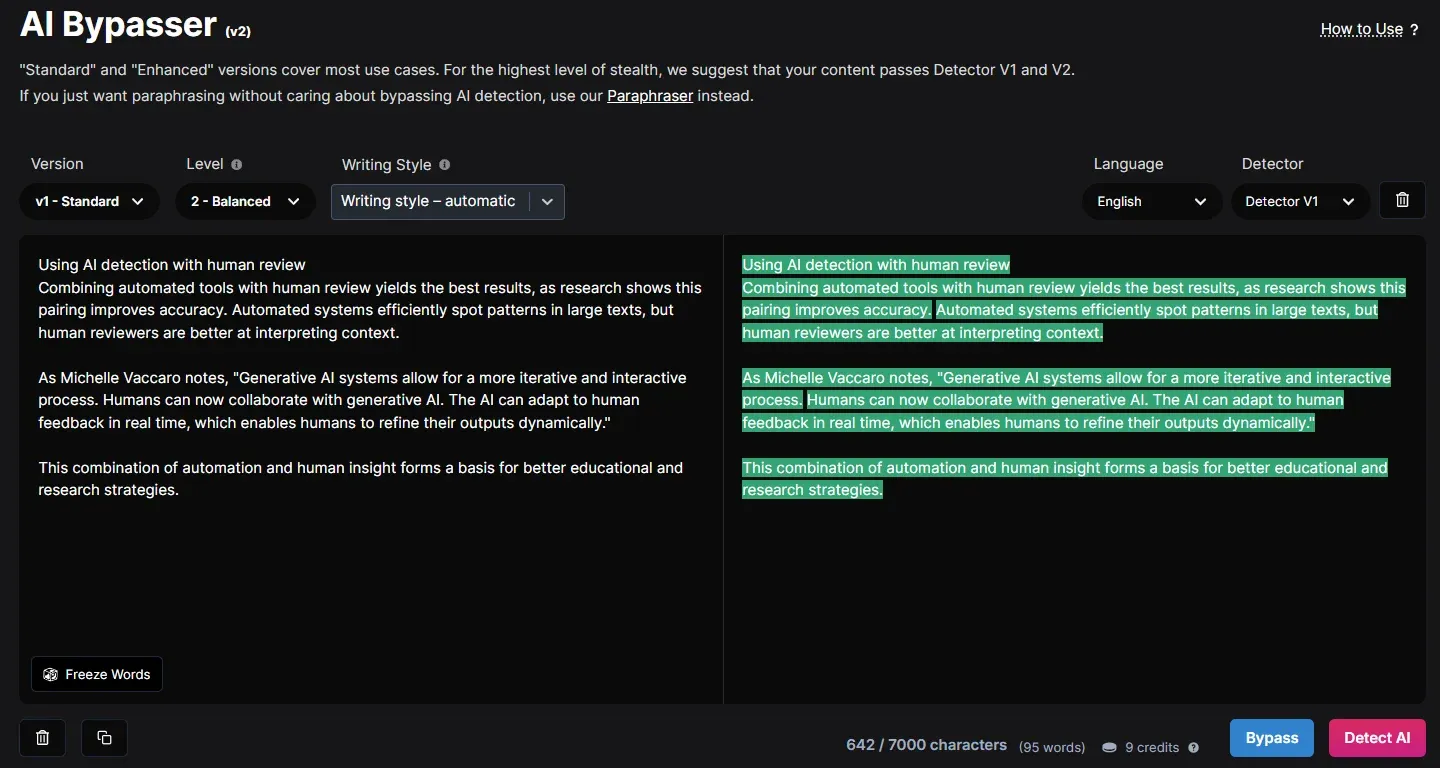
Using AI detection with human review
Combining automated tools with human review yields the best results, as research shows this pairing improves accuracy. Automated systems efficiently spot patterns in large texts, but human reviewers are better at interpreting context.
As Michelle Vaccaro notes, "Generative AI systems allow for a more iterative and interactive process. Humans can now collaborate with generative AI. The AI can adapt to human feedback in real time, which enables humans to refine their outputs dynamically."
This combination of automation and human insight forms a basis for better educational and research strategies.
Tips for teachers and researchers
Use AI detectors responsibly as a complement to human assessment, not a replacement. Build AI literacy, combine scores with writing style understanding and encourage open discussions.
Redesign assignments to focus on process and iterative feedback (e.g., multimodal projects). Continuously refine detection workflows to reduce errors. The goal is fostering growth and authentic academic voices, not just 'catching' students.
The Solution: Write → Test → Rewrite
This is where smart creators now work with a feedback system. With tools like Netus bypasser, you can:
- Scan your content in real-time
- See which parts are triggering red flags
- Rewrite just those blocks using AI bypass version, level and writing style
- Rescan until you hit “Human”
Instead of guessing, you’re testing and avoiding the pain of false positives entirely.
Final thoughts
AI detectors are fast but often inaccurate, frequently generating false positives that unfairly target diverse writers. They identify patterns, not comprehension, leading to inconsistency and bias. Future use needs a balance of automation and human insight.
Detectors should inform, not dictate, assessment, prioritizing context, intent, and human judgment. Education and work must enhance AI literacy and shift focus to critical thinking and process over just the final output.
For content creators navigating this complex landscape, a proactive feedback loop is essential. Tools like NetusAI can help close the gap between writing and detection by offering a Write → Test → Rewrite solution.
By allowing users to scan their content, identify flagged sections, and refine those specific blocks using advanced AI-bypass capabilities, Netus enables creators to ensure their authentic voice is preserved and prevent the issues associated with high false positive rates before submission.
FAQs
What are AI detectors and what is their primary function?
AI detectors basically check out the way something is written to figure out if a machine made it. You know, like spotting AI content.
Their main point is to help with stuff like keeping school papers real and honest. Also, they make sure the quality stays up there. Sometimes people overlook how these tools work on patterns.
Are AI detectors accurate?
From what I've read in some studies, AI detectors do not work that well in actual situations. They are kind of inconsistent, you know. Companies say their tools are super accurate, but then there are all these false positives where human writing gets flagged as AI.
What are the main types of errors AI detectors make?
The biggest problems with these detectors seem to be the false positives and false negatives. False positives are when something a person wrote gets flagged as AI by mistake.
That hits non-native speakers pretty hard, along with people who are neurodiverse or just have a more complicated way of writing. It feels unfair there.
What is the recommended best practice for using AI detectors effectively?
The best way to handle this is by mixing automated tools for detecting stuff with some real human checking. Like, you write something, then test it out using those tools to spot the weird parts.
How can content creators ensure their work is not incorrectly flagged as AI?
Creators who are smart about this stuff might try setting up a feedback system that works ahead of time. Like, they could do a loop where they write something, test it, and then rewrite based on what comes up.