You finally finished that blog post. It’s clean. Insightful. Maybe even a little poetic. But when you run it through an AI detector, it gets flagged.
Sound familiar?
Writers, students, marketers and even developers are running into the same issue in 2025:
AI content detectors often flag well-structured, polished human writing as AI-generated. by ChatGPT.
And here’s the twist:
These detectors aren’t asking, “Is this helpful?”
They’re asking, “Does this look machine-generated?”
Why It Happens
AI detectors don’t judge content based on availability of depth or quality. They scan for patterns, like sentence predictability, burstiness and perplexity, that mimic what large language models tend to generate.
So even if you wrote it, if it “feels” AI-like to the detector, it’ll get flagged.
And it’s not just frustrating, it’s disruptive:
- Students get accused of plagiarism.
- Freelancers lose credibility.
- Founders waste hours rewriting “clean” copy that fails an algorithm’s vibe check.
What Are AI Content Detectors?

By now, you’ve probably seen the warning labels: “This content may have been AI-generated.“
But how do detectors actually know?
Contrary to what many believe, AI detectors don’t run some magical truth scan.
They don’t catch ChatGPT red-handed. They simply analyze patterns and flag anything that matches what language models tend to produce.
The Core Mechanism
Most AI detectors, from ZeroGPT to HumanizeAI and Turnitin’s AI Writing Indicator, operate on the same basic logic:
AI-generated content has certain statistical fingerprints.
These tools look for traits like:
- Low burstiness (sentence variation)
- Low perplexity (predictability)
- Unusual syntactic uniformity
- “Machine” pacing and rhythm
Each sentence (or paragraph) is scored. If the scores fall within the typical range of LLMs like GPT‑4, the text is flagged, even if it was human-written.
Detectors Don’t Think, They Measure
To be clear: no detector is “intelligent.” They don’t understand context, story or nuance. They don’t see availability, just pattern probability.
This matters because human writing can easily fall within AI-like patterns, especially when it’s:
- Structured well
- Follows a logical outline
- Uses consistent tone and pacing
Ironically, the more professional your writing looks, the more it risks getting flagged.
The Science Behind Detection

Ever wonder why detectors flag a blog post that sounds perfectly human? It’s not intuition, it’s statistical modeling. AI detectors measure your writing using a set of scoring systems designed to catch the subtle patterns AI tends to repeat.
Perplexity: Measuring Predictability
At its core, perplexity is a measurement of how surprising each word in your sentence is, based on what came before it. If a language model expects the next word with high confidence, perplexity is low.
If it’s genuinely surprised by the next word, perplexity is high.
Why it matters:
- AI-generated text is very predictable. LLMs are trained to write smoothly, so their output tends to score with low perplexity.
- Human writers often introduce randomness, idioms or imperfect phrasing, raising perplexity scores.
That means your clean, well-outlined blog post?
It might be too perfect, which can backfire.
Burstiness: Sentence Variety
Burstiness measures variation in sentence length and structure.
- Humans write with natural rhythm. We ramble. We pause. We use short and long sentences interchangeably.
- AI, by default, tends to write with a steady, uniform rhythm unless prompted otherwise.
Detectors like ZeroGPT and HumanizeAI use burstiness scores to judge how much your sentence flow mimics human behavior.
Too symmetrical = suspicious.
Too varied = probably human.
Stylometric Patterns: Your Writing’s DNA
Beyond raw scores, detectors also tap into stylometry, the analysis of your writing “style” based on:
- Word frequency
- Punctuation habits
- Average sentence length
- Passive voice usage
- Syntax trees
These create a statistical fingerprint. Weber-Wulff et al. (2023) found stylometric models can detect unrewritten LLM content with up to 90% accuracy.
Even minor rewrites often don’t shift stylometric patterns enough to fool detection engines.
Why Good Writing Still Gets Flagged

Despite crafting clear, well-researched articles, AI detection in 2025 frequently misflags them as AI-generated, a frustrating issue.
This happens not because your work lacks human touch but because AI detectors aren’t measuring creativity. They’re measuring patterns.
The False Positive Problem
AI detectors aren’t perfect. And while their false-positive rates have improved, they still flag plenty of human-written content, especially when it’s:
- Highly structured
- Too consistent
- Clean and grammar-optimized
- Written by non-native English speakers
According to HumanizeAI, even their latest model can misclassify up to 1 in 100 human-written texts. That might sound low, until you consider the volume of essays, blogs and emails scanned daily.
Turnitin has acknowledged this as well, stating:
“AI writing indicators should not be used alone to make accusations of misconduct.”
The Hybrid Content Dilemma
Modern writing is often blended:
- You brainstorm in ChatGPT
- Add your own examples
- Rephrase and expand it by hand
The result? Hybrid content, partially AI-assisted, partially human.
But here’s the problem: Detectors don’t always separate the parts. If just 20–30% of your draft has LLM-style phrasing, the entire piece may be flagged.
Quillbot provides sentence-level analysis, while Turnitin only flags general probability, offering little clarity to writers.
When “Good” = “Too Clean”
Ironically, the more professional your writing sounds, the more likely it is to be flagged.
Why?
- AI tools are optimized for coherence, logic and rhythm
- Editors reinforce this
- Detectors see that polish and assume it’s machine-made
So you’re left in a weird place:
Write well and risk getting flagged. Write messy and look unprofessional.
The Solution: Write → Test → Rewrite
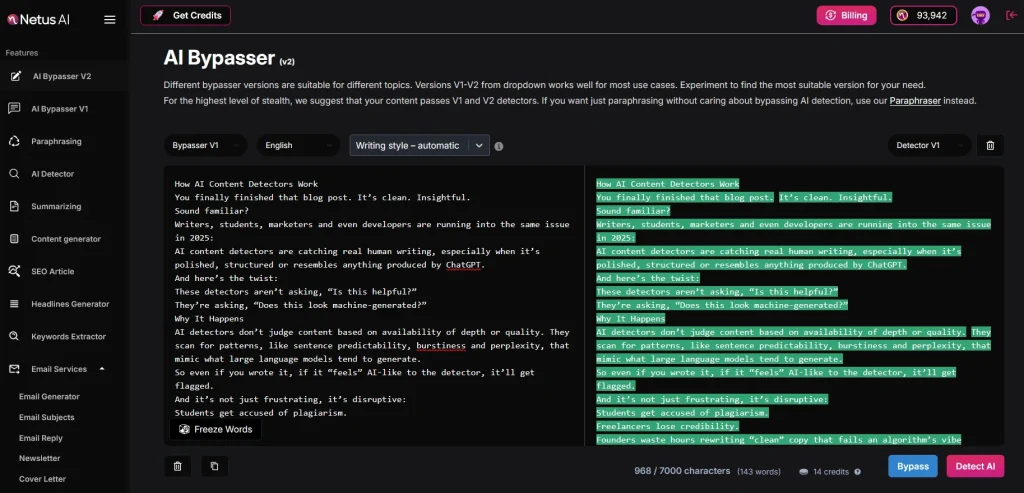
This is where smart creators now work with a feedback system.
With tools like Netus bypasser, you can:
- Scan your content in real-time
- See which parts are triggering red flags
- Rewrite just those blocks using AI bypass engines
- Rescan until you hit “Human”
Instead of guessing, you’re testing and avoiding the pain of false positives entirely.
Final Thoughts
AI content detectors aren’t going anywhere and they’re not always accurate. Students and marketers struggle to create quality content without triggering AI detection.
This is where Netus steps in, not as a magic wand, but as a realistic solution built for how people actually write. It is not just an AI content detector , it is
FAQs
1. Why does my content get flagged as AI even if I wrote it myself?
Because detectors look at structure, predictability and rhythm, not intent. If your writing is too polished, symmetrical or lacks variation, it may resemble AI-generated text. This happens especially with professional writing or when using tools like Grammarly.
2. Which is the most accurate AI content detector in 2025?
Tests show HumanizeAI and ZeroGPT lead in accuracy, both scoring 95–98% in recent comparisons. However, false positives are still common, especially for hybrid content (part-AI, part-human).
3. How can I avoid AI detection in my essays or blogs?
Use a tool that lets you rewrite with feedback. “Netus” offers real-time AI content detection and rewriting tools, ensuring your text passes as human-written.
4. Is it cheating to use AI for writing?
That depends on context. In academic settings, it can be considered misconduct. But in content creation or marketing, AI is just a tool. The key is to rewrite and refine outputs so they reflect your voice, not just machine structure.
5. Can AI detection tools recognize partially AI-written content?
Yes. Tools like ZeroGPT offer sentence-level detection and Turnitin flags percentage-based AI probability. If even 20–30% of your content reads as “AI,” the whole piece might be flagged. That’s why section-level rewriting matters.
6. What’s the difference between paraphrasing and true humanization?
Basic paraphrasers swap words. Netus’s advanced engine humanizes AI content, bypassing detection by restructuring sentences, varying rhythm and breaking AI patterns.
7. Can I check if my own writing looks like an AI before submitting it?
Absolutely. That’s exactly what tools like Netus are built for. You paste your draft, get instant AI/human verdicts and edit with rewriting engines, all without leaving the page.



