Understanding plagiarism
Plagiarism is the uncredited use of another’s intellectual property. Increased online publishing has led to a rise in plagiarism, prompting countries like Canada to enact strict protective laws.
Plagiarism harms both authors and creators, damaging credibility. In Canada, plagiarism is taken seriously with strict regulations protecting authors’ rights.
Using plagiarism checker tools helps writers ensure originality, fostering honesty and respect for intellectual property.
Varieties of plagiarism
Plagiarism, whether deliberate or accidental, can take many forms. Plagiarism includes direct copying and mosaic plagiarism, which substitutes synonyms without proper attribution.
Plagiarism also occurs when someone paraphrases or misquotes without citing the original source, even unintentionally.
Even accidental citation errors constitute plagiarism. Writers and students should use plagiarism detection tools to ensure their work is original and free of unintended overlap.
Understanding Canadian plagiarism laws
Canada, like other nations, addresses plagiarism through laws, primarily the Copyright Act. The 1921 Act, amended in 1988 and 1997, grants creators exclusive reproduction rights, protecting intellectual property.
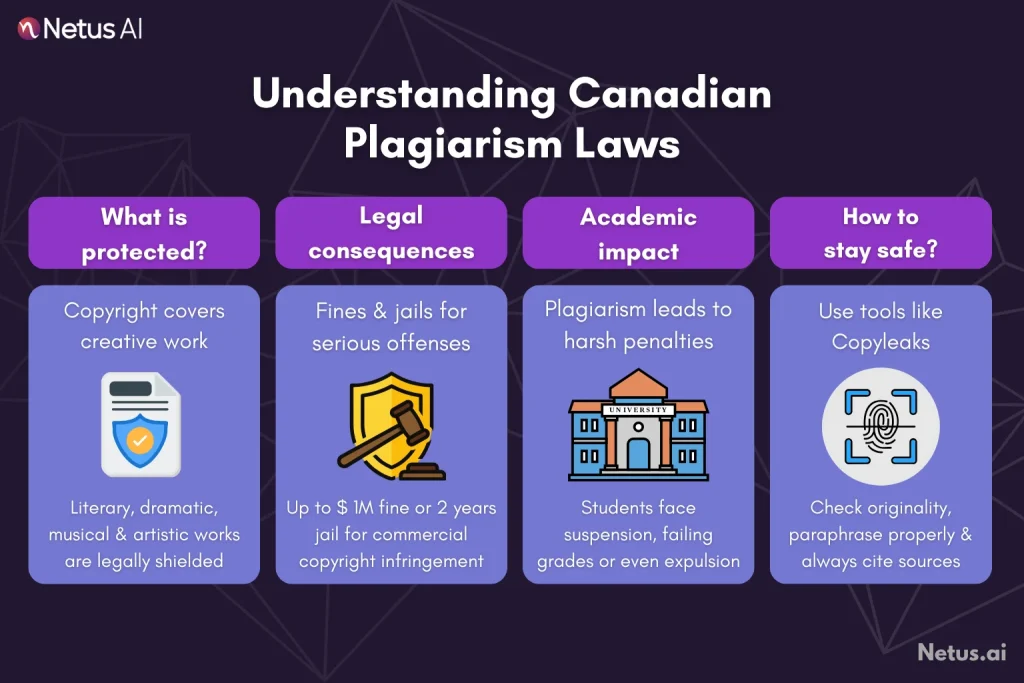
Copyright infringement involves the unauthorized duplication of an author’s work, violating their rights. The Copyright Act protects original literary, dramatic, musical and artistic works, giving authors exclusive rights to reproduce, publicly perform and adapt their creations.
Canadian law, as per Canadian Admiral Corp. vs. Rediffusion, mandates tangible and lasting identification for copyrighted works.
Section 12 of the Copyright Act protects Canadian government-created works for 50 years from their creation.
Canadian writers, academics and artists must understand and follow the Canadian Copyright Act and related regulations. This legal framework protects creators’ rights and promotes a fair, innovative environment in Canada.
What Is the punishment for plagiarism in Canada?
In Canada, the legal consequences of plagiarism vary depending on the severity and purpose of the infringement.
Under Section 35(1) of the Copyright Act, fines range from $100 to $5,000 for non-commercial violations. In cases of commercial infringement, the monetary penalty lies between $500 and $20,000.
Moreover, penalties become more severe for copyright infringement involving rental or sale of copyrighted materials. Offenders may face extended fines up to $1,000,000 and even imprisonment for up to 2 years. In instances of summary conviction, the consequences entail a fine of $25,000 and a possible 6-month jail sentence.
Educational institutions have strict anti-plagiarism policies. Students caught plagiarizing risk suspension, academic record damage and potential career harm. Institutions often assign failing grades for plagiarized work to uphold academic integrity.
Bloggers and content creators can also face legal issues if they use plagiarized content. Apart from potential legal consequences, the reputation and credibility of the content creators may be questioned. Their audience might lose faith in the quality and authenticity of the work, leading to a loss of readership.
Google policy for plagiarized content
Search engines like Google rigorously combat plagiarized content in an effort to enhance user experience.
Websites and blogs containing copied content might be removed from search results, leading to a substantial decline in traffic. For business blogs, the implications extend to tarnishing the organization’s reputation.
In summary, punishments for plagiarism in Canada vary depending on the nature and severity of the infringement. Consequences can range from fines and imprisonment to suspension, failing grades and lasting damage to reputations.
Understanding why detectors flag student work

AI detectors aren’t checking for plagiarism or intent. They’re scanning for writing patterns that resemble AI generated text. This is where most students get caught, often without realizing it.
Here’s what triggers academic AI detectors like Turnitin, ZeroGPT or HumanizeAI:
1. Overly predictable sentence structure (low perplexity)
AI-generated text flows in a highly predictable way. Detectors measure perplexity, a score that shows how easy it is to guess the next word in a sentence. If your sentences follow too smooth or robotic a flow, that’s a red flag.
2. Flat burstiness (little sentence variety)
Humans naturally vary their sentence lengths. A short punchy line here. A longer descriptive one there.
AI? Not so much. It often outputs sentences of similar length and rhythm. Detectors flag this lack of burstiness.
3. Stylometric fingerprints
Tools like Turnitin’s AI Writing Indicator analyze your unique writing style:
Your typical word choices, sentence length patterns, use of passive voice and even punctuation frequency. AI-generated content leaves statistical fingerprints that differ from most student writing styles.
4. Hybrid content risks
Many students blend AI and human writing:
- Brainstorm with ChatGPT
- Draft manually
- Polish with Grammarly
Detectors don’t separate the parts. Even if just 30% of your work feels AI-like, the whole document could get flagged.
How to stay safe and avoid plagiarism using NetusAI?
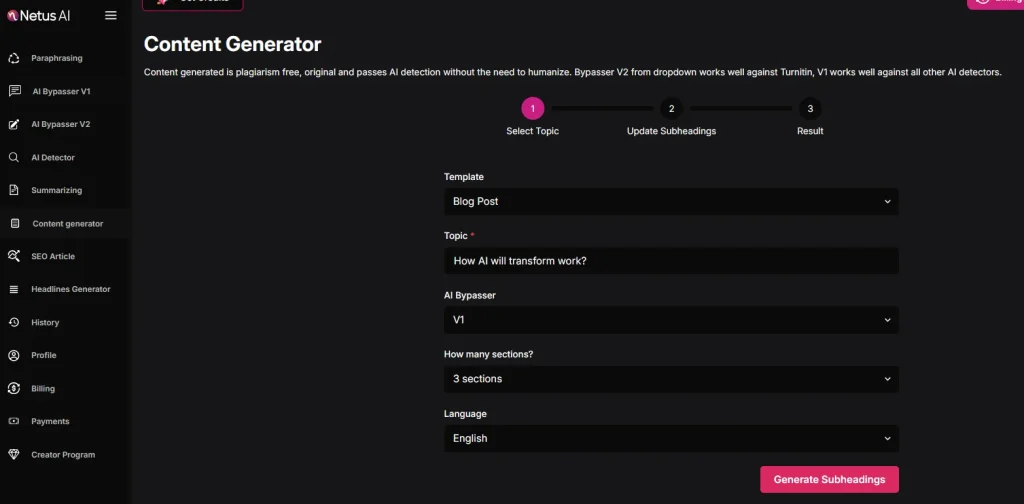
NetusAI offers a content generator that produces plagiarism-free content. Users can generate, download, copy and view their content history on the user-friendly NetusAI page.
NetusAI also offers detection and rewriting.
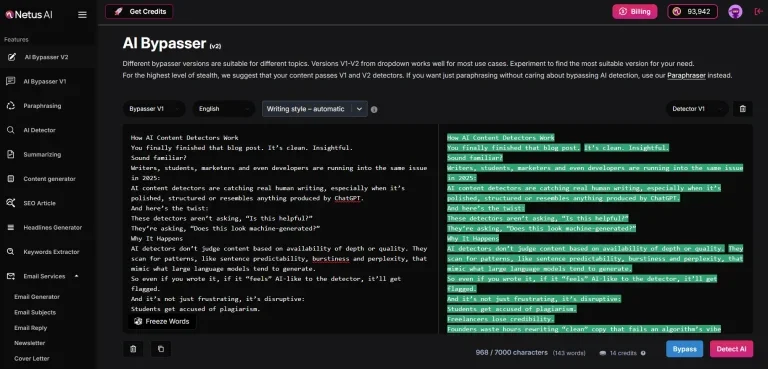
Why it’s safe for students:
- NetusAI bypasser is built around the exact patterns that AI detectors scan for (like perplexity and burstiness). Its real-time detection + rewriting loop helps you identify risky sections before submission.
- What you should use it for:
Rewriting flagged paragraphs, running final detection checks and tweaking tone and flow. - Caution:
Netus helps with structure and rhythm but always makes final edits in your own voice.
Final Thoughts
Plagiarism in Canada has serious legal and ethical implications. The Copyright Act protects intellectual property with penalties including fines and imprisonment. Academic and professional consequences range from suspension to reputational damage.
AI tools make plagiarism harder to understand. Everyone needs to know what plagiarism is and how these tools check their work.
NetusAI helps users create, detect and rewrite content to ensure originality and navigate AI detection. However, individuals are ultimately responsible for authentic voice and ethical standards. Combining knowledge of plagiarism laws and tools helps maintain integrity and values original thought.
FAQs
Plagiarism is the uncredited use of another person’s intellectual property, including direct copying, mosaic plagiarism, paraphrasing without citation and even accidental citation errors.
2. How is plagiarism addressed in Canada?
Canada addresses plagiarism primarily through the Copyright Act of 1921, which has been amended to grant creators exclusive reproduction rights and protect intellectual property.
3. What types of works are protected under the Canadian Copyright Act?
The Copyright Act protects original literary, dramatic, musical and artistic works, giving authors exclusive rights to reproduce, publicly perform and adapt their creations.
4. What are the financial penalties for plagiarism in Canada?
For non-commercial violations, fines range from $100 to $5,000. For commercial infringement, fines are between $500 and $20,000. More severe cases involving rental or sale of copyrighted materials can lead to fines up to $1,000,000.
5. Can plagiarism lead to imprisonment in Canada?
Commercial copyright infringement can lead to up to 2 years imprisonment or 6 months for summary convictions.
6. How do educational institutions in Canada deal with student plagiarism?
Plagiarism in education leads to suspension, academic and career damage and failing grades.
7. What are the consequences of plagiarism for bloggers and content creators?
Bloggers and content creators can face legal issues, damaged reputation and credibility and a loss of readership. Search engines may also remove their content from search results, leading to a decline in traffic.
8. Why do AI detectors flag student work?
AI detectors identify AI-generated text by looking for predictable sentence structures, lack of variety and unique stylistic patterns.
9. What are “stylometric fingerprints”?
Stylometric fingerprints are unique writing style patterns analyzed by tools like Turnitin’s AI Writing Indicator. Differences in word choice, sentence structure, passive voice use and punctuation can distinguish humans from AI generated content.
10. How can NetusAI help avoid plagiarism and AI detection?
NetusAI’s bypasser assists users in circumventing AI detection. It modifies AI-generated content in real-time to improve structure and rhythm, reducing flags.


