Picture this: your company’s content team spends a week polishing a white-paper draft. No ChatGPT involvement, just caffeine, style guides and a lot of Ctrl-S.
Minutes before publication, someone runs it through an AI-detection checker “just to be safe.” The verdict? “Highly likely AI-generated.” Cue the panic, edits and awkward Slack threads.
Scenarios like this aren’t edge cases anymore.
So, what’s really happening under the hood?
- Do detectors hold a secret list of GPT sentence fingerprints?
- Or are they gambling on statistical hunches that occasionally burn real writers?
Where ChatGPT Leaves Digital Footprints?

ChatGPT, even when prompted to write human-like text, leaves digital clues that AI detectors identify. These are the most common indicators:
Safety-First Vocabulary
LLMs are trained on vast public data, resulting in a neutral, easily understandable tone. They avoid overly fancy or casual language, slang, and special lingo, maintaining a consistent “neutral vibe” throughout.
Balanced Cadence in Lists
Ask ChatGPT for “10 tips,” and you’ll often get perfectly parallel sentences:
Tip 1: Do X.
Tip 2: Do Y.
Tip 3: Do Z.
Humans usually slip, adding an anecdote in one bullet, shortening another. Those imperfections boost burstiness; ChatGPT’s symmetry flattens it.
Filler Transitions
LLMs frequently use common phrases like “In today’s fast-paced world” as safe openings. Overusing these can trigger AI detection.
Temperature-Balanced Sentences
ChatGPT’s default “temperature” (0.7) creates a polished, predictable rhythm that persists unless deliberately altered or regenerated.
JSON-Like Structure in Explanations
ChatGPT’s predictable formatting, like JSON-like blocks or bulleted lists, makes it easily detectable by AI content detectors.
Why It Happens
AI detectors don’t judge content based on availability of depth or quality. They scan for patterns, like sentence predictability, burstiness and perplexity, that mimic what large language models tend to generate.
So even if you wrote it, if it “feels” AI-like to the detector, it’ll get flagged.
And it’s not just frustrating, it’s disruptive:
- Students get accused of plagiarism.
- Freelancers lose credibility.
- Founders waste hours rewriting “clean” copy that fails an algorithm’s vibe check.
What Are AI Content Detectors?
By now, you’ve probably seen the warning labels: “This content may have been AI-generated.”
But how do detectors actually know?
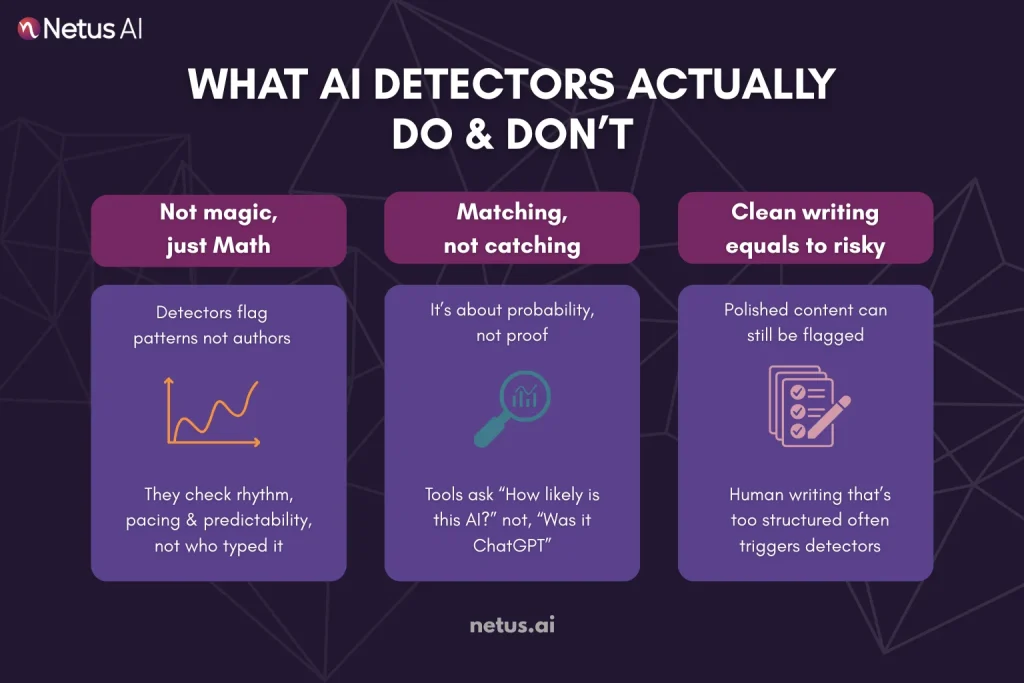
AI detectors analyze patterns in text, not truth, to identify content likely generated by language models.
The Core Mechanism
Most AI detectors, from ZeroGPT to HumanizeAI and Turnitin’s AI Writing Indicator, operate on the same basic logic:
AI-generated content has certain statistical fingerprints.
These tools look for traits like:
- Low burstiness (sentence variation)
- Low perplexity (predictability)
- Unusual syntactic uniformity
- “Machine” pacing and rhythm
Each sentence (or paragraph) is scored. If the scores fall within the typical range of LLMs like GPT‑4, the text is flagged, even if it was human-written.
It’s Not About “Catching AI”, It’s About Matching Probability
Here’s what AI detection isn’t:
- It’s not forensic text analysis
- It doesn’t detect if ChatGPT or Claude wrote your piece
- It doesn’t judge your intent
Instead, it answers:
“How likely is it that this was generated by a bot?”
If your writing feels too clean, too consistent, too symmetrical, it starts to resemble AI output. And that’s where even human-written essays and blogs can fail.
Detectors Don’t Think, They Measure
To be clear: no detector is “intelligent.” They don’t understand context, story or nuance. They don’t see availability, just pattern probability. This matters because human writing can easily fall within AI-like patterns, especially when it’s:
- Structured well
- Follows a logical outline
- Uses consistent tone and pacing
Ironically, the more professional your writing looks, the more it risks getting flagged.
The Solution: Write → Test → Rewrite
This is where smart creators now work with a feedback system.
With tools like NetusAI bypasser , you can:
- Scan your content in real-time
- See which parts are triggering red flags
- Rewrite just those blocks using AI bypass engines
- Rescan until you hit “Human”
Choose from two rewriting engines:
- for fixing sensitive paragraphs
- for polishing full sections
Instead of guessing, you’re testing and avoiding the pain of false positives entirely.
Final Thoughts:
By now, one thing’s clear: AI detectors don’t care how long you spend writing. They don’t know if you used ChatGPT, Grammarly or just years of good writing habits.
AI detection identifies content with specific patterns, low perplexity, uneven burstiness, or stylometric fingerprints, indicating it deviates from human-like statistical norms.
Whether you’re a student, marketer, founder or freelance writer, fighting false flags isn’t about writing less clearly. It’s about testing, adjusting and rewriting with intent.
NetusAI is pretty cool for content creators. It’s like a safety net that helps you check, rewrite, and retest your content in real-time, so you can get your scores just right before you hit submit.
You can see your AI risk before your professor, editor or Google’s algorithms do.
FAQs
1. Can AI detectors directly identify ChatGPT usage?
No. AI detectors don’t track your ChatGPT history or check your OpenAI account. They analyze patterns like perplexity, burstiness, and stylometry in the text itself to predict if it’s AI-generated.
2. Why does my human-written content still get flagged as AI?
AI detectors can mistake predictable, unvaried human writing (like SEO-optimized or Grammarly-processed text) for AI-generated content.
3. Do detectors like ZeroGPT and Turnitin compare text to a ChatGPT database?
No. These tools don’t have access to ChatGPT’s training data or your chat history. They rely on probability models and writing-pattern analysis—not content-matching.
4. Will rewriting a few sentences help me avoid detection?
Not always. Small edits or synonym swaps won’t break deep AI patterns. To reduce detection risk, you’ll need structural rewriting—changing sentence rhythm, tone, and flow. Tools like NetusAI specialize in this kind of advanced rewriting.
5. Is Grammarly making my writing too AI-like?
AI detectors might identify overly polished content, so maintaining natural writing quirks helps.
6. Can changing ChatGPT’s temperature setting help bypass detectors?
Lowering or raising ChatGPT’s temperature can alter randomness in output, but it’s not a guaranteed fix. Even high-temperature outputs can carry detectable stylometric patterns.
7. What’s the safest workflow for publishing AI-assisted content?
A good practice is:
- Draft (AI or human)
- Run through a detector like NetusAI
- Rewrite flagged sections
- Retest
This detect-rewrite-retest loop greatly reduces your risk of false positives.
8. Can detectors spot hybrid content (part AI, part human)?
Yes, and this is becoming more common. Even if only 20-30% of your draft is AI-generated, it may still push your detection score into the red.
9. Are there 100% foolproof ways to bypass all detectors?
NetusAI’s Bypasser V2 is super good at detecting stuff because it looks at detection patterns and AI footprints. This makes your content way safer than just basic paraphrasing.
10. Should I be worried about watermarking in ChatGPT outputs?
As of mid-2025, OpenAI hasn’t implemented widespread token-level watermarking in ChatGPT. However, future detectors might use advanced fingerprinting, making humanization tools a smart proactive measure.