As AI becomes more prevalent, so too do terms like natural language processing (NLP).
- Have you ever considered the underlying mechanisms that enable computers to “process” natural language and what that process entails?
- How does NLP facilitate human-computer communication?
- How are these elements combined to form coherent sentences and phrases?
Explore natural language processing: its scope and the innovations and practices researchers are pursuing as artificial intelligence advances.
Text pre-processing: The critical first step

Raw text data often includes extra code and formatting, hindering computer interpretation. Pre-processing is the initial step that transforms raw text into a clean, understandable format.
For example, one study looked at how to clean up online text by getting rid of things like HTML tags, scripts or ads.
Tokenization
Computers process information differently from humans, struggling with the nuances of sentences and paragraphs. Tokenization is crucial for processing varied word and line structures.
Tokenization is the process of dividing text into individual units or tokens, which allows for independent machine analysis.
According to Coursera’s guide on Tokenization in NLP, tokens can encompass:
- Words
- Specific characters
- Phrases
- Sentences
POS tagging
POS tagging assigns grammatical categories (nouns, verbs, adjectives) to words in a sentence. This Encyclopedia of Machine Learning technique helps machines categorize words and understand their relationships, providing essential context.
For example, the word “run” in English can function as both a noun (e.g., “I went for a run”) and a verb (e.g., “I run every day”). Part-of-speech (POS) tagging helps to clarify the intended meaning of such words within their specific context.
Identifying named entities
Named Entity Recognition (NER) is a key component in Natural Language Processing. NER categorizes words into entities like “person,” “location,” or “organization,” as defined by MIT Press Direct.
This allows the system to differentiate between “Apple” (the company) and “apple” (the fruit).
It allows the system to distinguish between “Apple” as a brand and as a food.
Exploring syntax and semantics
Even after segmenting the text and categorizing words by type (e.g., nouns, verbs), the process is not yet complete.
Machines must grasp both syntax and semantics. Syntax refers to the arrangement of words in a sentence to convey meaning.
In NLP, semantics is a machine’s ability to understand word meanings in sentences. Semantic processing allows an NLP model to decipher a phrase’s meaning by analyzing surrounding words for context.
NLP: Language generation
After text and semantic pre-processing, language generation is the subsequent step in NLP. AI users input queries; the tool generates linguistic/textual responses based on its training.
Everyday applications of NLP
Now that you understand NLP, what are its applications? This transformative technology is already integrated into various aspects of our daily routines.
Integrated into Google searches
NLP is at work every time you use Google or other search engines. It helps these engines grasp the intent behind your search. For instance, if you type “How to fix a cracked phone screen,” NLP understands you’re looking for instructions, not just general information.
Google isn’t alone in utilizing AI for search; other search engines do as well. Explore our guide on AI Search Engines to learn more.
Chatbots and virtual assistants
AI chatbots and virtual assistants are also powered by natural language processing.
In customer service, an AI chatbot can address customer inquiries using a knowledge base, tutorials or FAQs. If the chatbot cannot resolve the issue, it can then escalate the request to a human agent.
Recommendations for streaming content
Netflix uses machine learning and natural language processing to suggest content based on viewing habits.
Advances in healthcare
Natural Language Processing (NLP) and machine learning are increasingly integrated into healthcare. For example, the Yale School of Medicine recently highlighted a new book on NLP in Biomedicine. This publication explores NLP’s potential in clinical text analysis and biomedical applications.
Natural language processing: Current challenges
Despite its advancements, NLP still faces challenges and issues.
- Data privacy is a significant concern.
- As NLP technology advances, careful consideration must be given to the large datasets required for its training.
- Closely monitoring data is crucial to prevent the training of AI models on inherent biases.
The future of NLP: What lies ahead?
Looking ahead, current research continues to push the boundaries of what’s possible with NLP and the broader field of AI. Key areas of advancement include:
- Explainable AI (XAI): As NLP models become more complex, Explainable AI (XAI) is crucial for understanding their decisions. So, what exactly is XAI? Carnegie Mellon University defines it as research focused on helping people grasp and trust machine learning.
- Responsible AI practices: As AI technology advances, establishing a framework for its responsible use becomes crucial. Stanford University provides an excellent guide on safe and responsible AI practices for the university.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a dynamic and ever-evolving field that integrates computer science, linguistics and artificial intelligence. Its primary goal is to enhance human-to-computer interactions, making them feel more intuitive and natural.
What NetusAI is doing in NLP
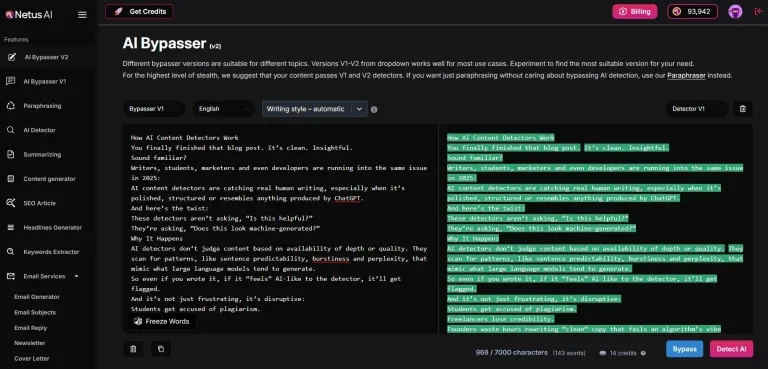
NetusAI leads the way in using NLP to develop cutting-edge tools that improve content creation and analysis. Our platform utilizes advanced NLP techniques to provide solutions that include:
- Our NLP models detect AI-generated text, helping users distinguish human from machine-authored content.
- Our AI Bypasser uses NLP to grasp your meaning. Regular checkers often miss that.
- Our NLP-powered paraphrasing tools enable users to rephrase text effectively, preserving its original meaning and context. This helps in generating distinctive and engaging content.
- Leveraging NLP, our summarization tools extract key information and generate concise summaries of long texts, enhancing information accessibility and saving users time.
NetusAI improves NLP tools to boost digital content authenticity, efficiency and quality for individuals and businesses.
Final thoughts
Natural Language Processing is an exciting and rapidly advancing field at the intersection of AI, computer science and linguistics.
NLP’s capacity to empower computers to comprehend, analyze and produce human language has resulted in its widespread adoption across numerous everyday applications. These range from search engines and virtual assistants to applications in healthcare and entertainment.
NLP is constantly getting better, tackling challenges like data privacy and bias by exploring explainable AI and responsible AI. This is leading to more natural ways for us to interact with computers.
NetusAI helps NLP by offering tools that make digital content more real, efficient and better quality.
FAQs
What is Natural Language Processing (NLP)?
NLP, an AI branch, enables computers to understand, interpret and generate human language, improving human-computer interactions.
Why is text pre-processing important in NLP?
NLP begins with text pre-processing, transforming raw, often extraneous, text into a clean, computer-interpretable format.
Tokenization breaks text into analyzable units (words, characters, phrases or sentences) called tokens.
How does POS tagging help in NLP?
POS tagging assigns grammatical categories (nouns, verbs, adjectives) to words, helping machines understand word relationships and meaning within context.
What is Named Entity Recognition (NER)?
NER in NLP categorizes words (e.g., “person,” “location,” “organization”) to distinguish homophones like “Apple” (company) and “apple” (fruit).
What is the difference between syntax and semantics in NLP?
Syntax governs word arrangement for meaning, while semantics enables machines to understand word meanings through contextual analysis.
What are some everyday applications of NLP?
NLP is integrated into Google searches, chatbots, virtual assistants, streaming content recommendations and healthcare advancements.
What are the current challenges in NLP?
NLP faces challenges with data privacy, large dataset management for training and preventing AI bias.
What does the future of NLP hold?
NLP’s future includes Explainable AI (XAI) for user trust and responsible AI practices for ethical use.
NetusAI uses NLP for tools like AI Content Detection, Paraphraser and Summarizer, improving digital content authenticity, efficiency and quality.




